Table of Contents
ToggleRadio Frequency Identification (RFID)
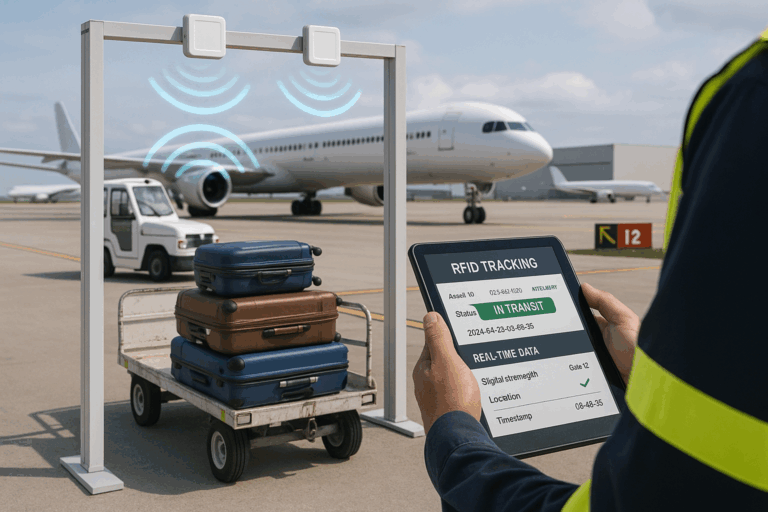
The RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) system is an innovative technology that has been rapidly expanding its operations across various sectors. The system is composed of tags, an antenna, and readers. The reader scans the tag and transfers the information to the antenna, making it a seamless process that can lead to less waste, reduced costs, and increased productivity and profitability for the company and its assets.
RFID technology provides numerous benefits for identifying and tracking products and services through radio frequency. This technology is user-friendly, fast in reading and transmitting data, and has the ability to integrate with other platforms, making it a flexible solution for various business needs. RFID technology has become fundamental for companies, from production control to logistics management, due to its efficient information identification capabilities.
In general, RFID technology transforms the way businesses operate and can provide significant advantages over traditional tracking and identification methods. By adopting RFID technology, companies can streamline their operations and gain a competitive edge in today’s fast-paced business environment.
What Is RFID?
RFID stands for Radio Frequency Identification, which is a technology that uses radio waves to identify and track objects that are tagged with RFID tags or labels. RFID tags are small electronic devices that store information, such as product details, inventory information, or tracking data, and can be attached to a wide range of items, from retail products to manufacturing equipment.
What Is an RFID System?
RFID Systems utilizes from a technology that uses radio waves to identify and track objects. This works by using radio waves to transmit data between the RFID reader and the RFID tag. An RFID system typically consists of three main components:
- RFID tags or labels: These are small electronic devices that store information, such as product details, inventory information, or tracking data. RFID tags can be attached to a wide range of items, such as retail products, manufacturing equipment, or vehicles.
- RFID reader: This is a device that sends out a radio signal to activate the RFID tag and receive the information stored on it. RFID readers can be handheld or mounted on a fixed location, such as a wall or a conveyor belt.
- Backend software or system: This is the software or system that processes the data received from the RFID reader and uses it for various purposes, such as tracking inventory, monitoring the location of goods in transit, or authenticating products in a retail store.
The reader sends out a radio signal that identifies and tracks the tag, which then responds with its unique identification information. This information is then sent back to the reader, which processes the data and sends it to the backend software or system for further analysis and use.
How does RFID loss prevention technology work?
RFID technology has been widely used in stores as an effective loss prevention system. Companies can label their inventory with RFID tags to identify and track item movement in real-time across different areas, as well as monitoring inventory levels.
RFID loss prevention technology can help reduce inventory shrinkage and prevent theft, which can save retailers significant costs and resources. In general, RFID tags are used to track inventory levels, monitor product movement within a store, improving supply chain operations.
What is RFID inventory management?
An organization’s inventory management is a critical aspect of its operations since it is directly related to changes in working capital. Proper inventory management provides accurate data on customer demand, inventory shipping, and internal controls across the supply chain.
RFID-based inventory management is a more efficient and reliable option in terms of reducing errors. This system consists of RFID tags that digitizes product information, including expiration and manufacturing dates. The RFID system uses radio frequency to store and control all information of the RFID tags. This information is then transmitted via radio waves to an antenna and integrated with the receiver, which reads and converts it into useful data. With RFID inventory management, companies can streamline their operations, reduce errors, and improve accuracy, leading to increased productivity and profitability.

What is an RFID tag?
An RFID tag is also known as “Smart Label” or “Smart Tag”, which is a label that contains a RF (radio frequency) microchip enabling it to communicate with an RFID reader and antennas for tracking and identification purposes.
RFID tags can be either active or passive. Active tags have a power source and can transmit their own signal to the reader, while passive tags do not have their own power source and rely on the reader to send a signal to the tag to power it and receive the tag’s signal. RFID tags can store various types of information such as a unique identifier, product information, expiration dates, and more. This information can be read and processed by an RFID reader, which can be stationary or handheld.
What are the different types of UHF RFID tags (passive Tags)?
Standard UHF RFID tags are the most common type of UHF tags and are designed for general use. They operate in the frequency range of 860-960 MHz and have a read range of up to 10 meters.
Near-field UHF RFID tags operate in the frequency range of 865-868 MHz and are designed for use in close proximity to the reader. They have a read range of up to 1 meter.
Far-field UHF RFID tags operate in the frequency range of 902-928 MHz and are designed for use in applications where longer read ranges are required. They have a read range of up to 30 meters.
High-temperature UHF RFID tags are designed to operate in high-temperature environments, such as in manufacturing and industrial applications. They can withstand temperatures of up to 200°C.
Metal-mount UHF RFID tags are designed for use on metal surfaces, which can interfere with the RFID signal. They are commonly used in asset tracking and inventory management applications.
Can RFID tags be reused or reprogrammed?
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) tags are small electronic devices that use radio waves to communicate with nearby RFID readers. They consist of a microchip and an antenna, and are used for a variety of applications, including inventory tracking, access control, and payment systems.
Yes, RFID tags can be reused and reprogrammed. The ability to reuse and reprogram RFID tags is a key advantage of this technology. There are different types of RFID tags available, and the ability to reuse and reprogram them depends on the type of tag and the intended use case.
How long does an RFID tag last?
The lifespan of an RFID tag depends on several factors, including the type of tag, the environment in which it is used, and the frequency of use. Passive RFID tags, which do not have a battery, often have a typical lifespan of around 50,000 reading cycels. Active RFID tags, which have a battery, can last longer than passive RFID tags. The lifespan of an active RFID tag can range from 3-10 years, depending on the battery and the frequency of use. The battery in an active RFID tag may need to be replaced or recharged periodically to maintain the tag’s functionality.
How to select the right RFID Tag?
Choosing the right type of RFID label is an important decision, as it can significantly impact the efficiency and accuracy of the RFID system. While there are many types of RFID tags available, the choice ultimately depends on the specific industry and use case.
Working with a manufacturer and applicator of RFID solutions can be beneficial in selecting the appropriate RFID label. They can provide guidance on the type of label that will best meet the requirements of the industry and use case.
To choose the appropriate RFID labels or tags for a project, customers should consider the use case and inform the RFID solutions provider if the tags will be applied to metal or non-metal surfaces. Hybrid labels and on-metal tags are suitable for both metal and non-metal surfaces, ensuring an exceptional reading performance. Customers should also differentiate between active and passive RFID tags and specify the operating environment to ensure the tags withstand harsh conditions. RFID tags can be printed with unique identifiers like barcode serial numbers or QR codes, and various formats and dimensions are available, including labels, hangtags, woven, and hard tags. Providing detailed information contributes to identifying the correct RFID solution for each unique application.



























