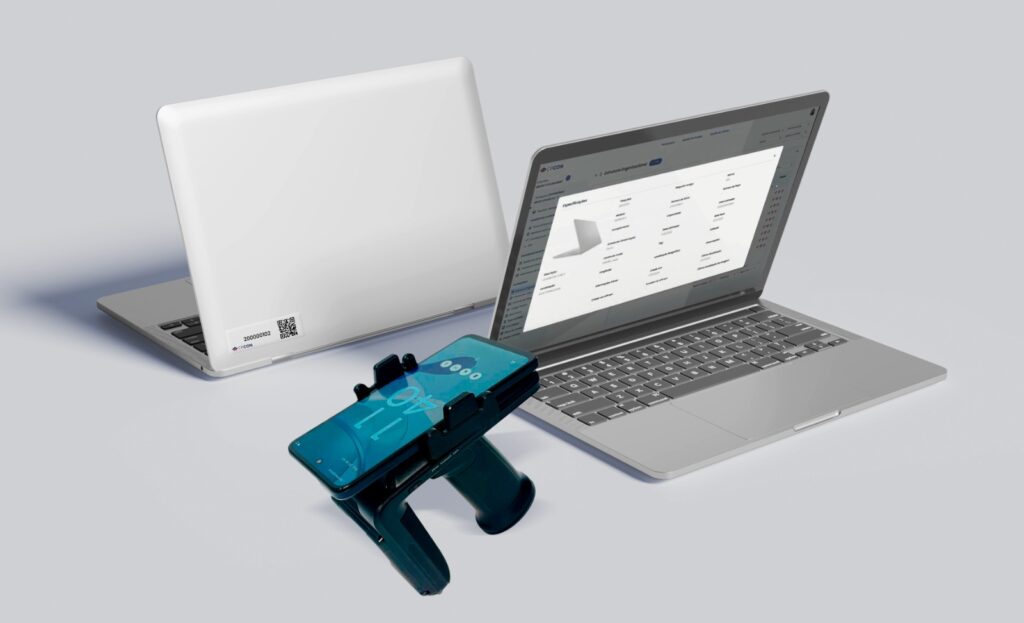
What is fixed asset accounting? Fixed asset accounting refers to the management and control of tangible assets — such as machinery, vehicles, and furniture — that are used in business operations for periods longer than one year. These assets directly impact the balance sheet, asset depreciation, and the overall financial health of an organization.
However, the emergence of ghost assets presents a silent but serious challenge, undermining accounting accuracy and creating hidden costs. In this guide, we explore how to identify and manage fixed assets effectively, prevent inventory distortions, and promote strong financial compliance.

Table of Contents
ToggleWhat are ghost assets?
Ghost assets are items that remain recorded in a company’s financial statements but are no longer physically present or usable.
Examples include scrapped equipment, stolen vehicles, or furniture that was discarded without proper accounting write-off.
Even though these assets no longer exist, they continue to generate unnecessary costs — such as improper depreciation, insurance payments, and excessive taxation.
Practically speaking, ghost assets create a disconnect between operational reality and financial records, impairing planning accuracy and transparency.
Main causes of ghost assets
The formation of ghost assets is typically linked to failures in asset management processes. The most common causes include:
- Unrecorded asset disposals: Sales, donations, or scrapping of assets that are not properly updated in the financial system.
- Manual tracking errors: The use of spreadsheets or paper records increases the risk of inconsistencies and oversight.
- Infrequent audits: A lack of regular physical inventory counts allows discrepancies between records and reality to go unnoticed.
- Unreported theft or loss: Stolen or misplaced assets that remain recorded in the books.
- Partial dismantling of assets: Equipment dismantled for spare parts but still accounted for as a complete asset.
These factors highlight the need for robust corporate asset control systems to ensure accurate records and safeguard financial integrity.
The impact of ghost assets on your business
The presence of ghost assets creates significant risks across multiple areas:
- Overstated asset value: Financial statements reflect an inflated value, undermining credibility.
- Increased costs: Companies continue paying taxes and insurance premiums on non-existent assets.
- Inefficient planning: Strategic decisions are based on inaccurate inventory data
- Financial compliance risks: Record-keeping inconsistencies may lead to audit issues and regulatory penalties.
Ignoring these risks can damage profitability, operational efficiency, and investor confidence.
How to identify ghost assets
Detecting ghost assets requires a proactive and structured approach. Best practices include:
- Conducting regular physical inventories: Physically verify the existence and condition of listed assets.
- Implementing asset tracking technologies: Solutions such as RFID asset tracking allow for real-time monitoring and control.
- Reconciling accounting and operational records: Cross-check inventory findings against financial data to catch discrepancies.
- Using asset management software: Automated systems reduce errors and improve asset lifecycle visibility.
These practices help organizations quickly detect inconsistencies and strengthen overall asset management processes.

Strategies to prevent ghost assets
The best way to deal with ghost assets is to prevent their formation. Key prevention strategies include:
- Adopting asset tracking technologies: Barcode and RFID tagging simplify asset identification and tracking.
- Implementing asset lifecycle management systems: Document each phase, from acquisition to disposal.
- Scheduling regular audits: Frequent physical inventories correct discrepancies early.
- Training responsible teams: Educate employees on best practices for asset tracking and recordkeeping.
- Standardizing asset disposal procedures: Ensure all sales, donations, or disposals are formally documented and updated.
These actions strengthen governance and contribute to cost reduction strategies and operational excellence.
The importance of physical inventory in fixed asset accounting
Maintaining an accurate physical inventory is fundamental for effective fixed asset accounting. The main benefits include:
- Verification of asset existence and condition: Ensures financial statements accurately reflect operational reality.
- Updated location and status records: Facilitates efficient asset utilization.
- Correct depreciation calculations: Aligns accounting entries with actual asset life cycles.
Neglecting physical inventory increases exposure to financial, operational, and regulatory risks.
CPCON: Intelligent Solutions to Eliminate Ghost Assets
CPCON is a leading provider of integrated fixed asset management solutions, helping organizations eliminate ghost assets and strengthen corporate asset control.
Our services include:
- Advanced RFID asset tracking systems: Real-time visibility and high-precision asset monitoring.
- Customized physical inventories: Tailored to the operational reality of each client.
- Specialized consulting in financial compliance: Ensuring adherence to key accounting and regulatory requirements.
With CPCON’s expertise, companies transform asset control into a competitive advantage, enhancing operational efficiency and ensuring full financial compliance.
Conclusion
Accurate fixed asset accounting is essential for maintaining financial integrity, reducing unnecessary costs, and ensuring compliance with regulations.
By eliminating ghost assets and implementing strong asset management practices, organizations improve governance and create a solid foundation for sustainable growth.
With CPCON’s support, your company can achieve reliable asset lifecycle management, optimize performance, and build long-term financial resilience.
Ready to take full control of your fixed assets?
Eliminate ghost assets, strengthen your financial compliance, and unlock operational efficiency with CPCON’s specialized solutions.
Contact our experts today and discover how we can help transform your fixed asset accounting into a true competitive advantage.
FAQ – Fixed Asset Accounting and Ghost Assets
What is a ghost asset?
A ghost asset is an item that remains recorded in a company’s financial statements but no longer physically exists or is no longer usable.
How do ghost assets impact financial statements?
They inflate asset values, distort balance sheets, and result in unnecessary tax and insurance costs.
What is the best way to detect ghost assets?
Conduct regular physical inventories and reconcile findings with accounting records.
How does asset tracking technology help prevent errors?
Solutions like RFID asset tracking enable real-time updates, reducing discrepancies and improving inventory accuracy.
What are the signs that a company needs to review its asset management practices?
Misalignment between inventory and accounting records, frequent manual write-offs, and inconsistencies flagged during audits.
What role does asset depreciation play in fixed asset accounting?
Depreciation reflects the gradual loss of asset value over time, directly impacting profit margins and tax liabilities.
How can CPCON support fixed asset management?
By offering specialized physical inventories, advanced tracking technologies, and strategic consulting services to ensure accurate fixed asset accounting and financial compliance.